In precision manufacturing and product design, small components often play a big role in safety, performance, and ease of assembly. One such unsung hero is the captive screw — a simple yet critical fastener used across aerospace, electronics, defense, medical devices, and industrial machinery.
In this article, we’ll explore what captive screws are, how they work, why they’re used, and how to choose the right one for your application.
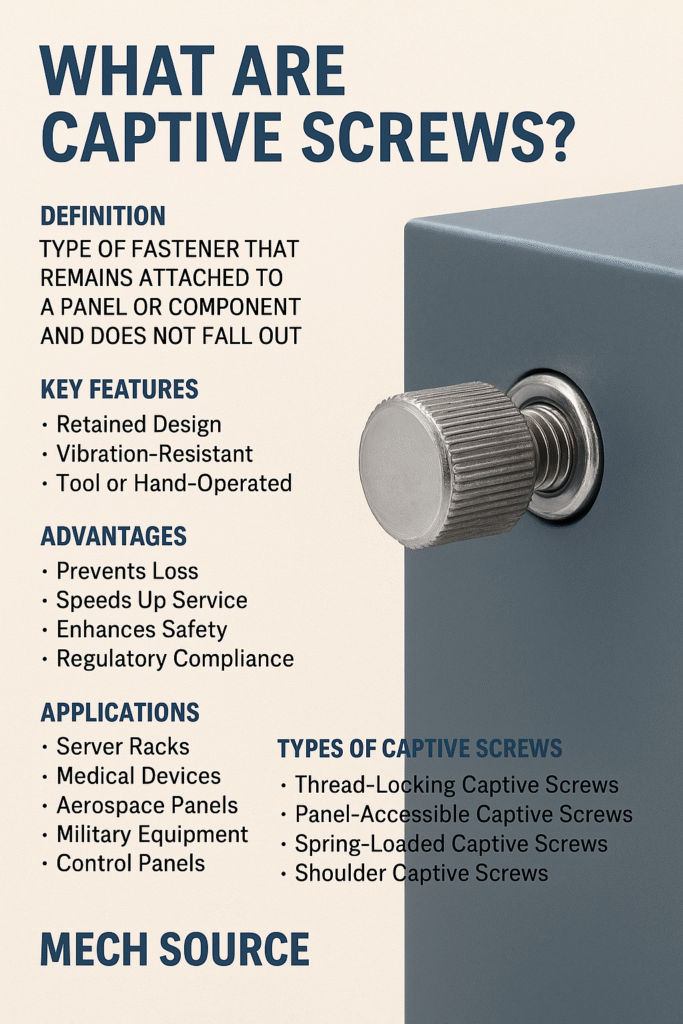
What Is a Captive Screw?
A captive screw is a type of fastener that is permanently retained within a panel, enclosure, or equipment cover — even when it is unscrewed from its mating thread.
Unlike regular screws that can fall out or get lost during servicing, captive screws remain “captive” to the component they fasten, improving safety, efficiency, and compliance.
Example: Think of access panels on telecom or medical equipment — when the screws are loosened, they don’t fall off. That’s a captive screw in action.
Key Features of Captive Screws
Retained Design: The screw stays fixed in the panel even when disengaged from the mating thread.
Reduced FOD (Foreign Object Debris): Essential in aerospace and defense where loose parts can pose critical risks.
Tool- or Hand-Operated: Available with slotted, Phillips, hex, thumb, or knurled heads.
Vibration-Resistant: Many designs include self-retaining washers or spring mechanisms.
RoHS & REACH Compliant: Available in environmentally compliant materials and finishes.
Common Applications
Server racks and IT enclosures
Medical devices
Aerospace panels
Military equipment
Control panels
Instrumentation covers
Advantages of Using Captive Screws
✅ Prevents Loss: Reduces the risk of losing screws during maintenance or assembly.
✅ Speeds Up Service: Saves time for technicians, especially in field servicing.
✅ Enhances Safety: Prevents falling screws that could damage electronics or pose safety risks.
✅ Regulatory Compliance: Required by MIL and DIN standards in aerospace and defense.
✅ User-Friendly: Ideal for access panels where frequent opening and closing is expected.
Types of Captive Screws
Thread-Locking Captive Screws
Held in place by thread locking features or retention rings.Panel-Accessible Captive Screws
Feature oversized knurled heads or winged designs for tool-less operation.Spring-Loaded Captive Screws
Include compression springs for smooth retraction and return.Shoulder Captive Screws
Use an unthreaded shoulder section to retain the screw in the panel.
Materials and Finishes
Stainless Steel (304, 316) – Corrosion resistance, ideal for medical and marine use.
Aluminum – Lightweight applications.
Carbon Steel – Cost-effective with zinc or black oxide coating.
Plastic/Polymer Screws – For non-conductive or lightweight assemblies.
Choosing the Right Captive Screw
Here are some factors to consider when selecting a captive screw:
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Application | Is it for access, safety, or vibration control? |
| Environment | Exposure to moisture, heat, or chemicals? |
| Operation Type | Tool-driven or hand-driven? |
| Panel Thickness | Choose retention hardware that matches. |
| Thread Size | Matches the tapped hole or captive nut. |
Captive Screws at Mech Source
At Mech Source, we specialize in precision machined fasteners, including custom and standard captive screws.
✔️ Customized to Your Drawings
✔️ Material Certifications
✔️ Batch Traceability
✔️ Small Batch Production
✔️ Tight Tolerances (±0.01 mm)
Whether you need captive screws for electronics, defense assemblies, or custom enclosures, our team can support you with high-quality, on-time components.
Need Custom Captive Screws?
🔩 Mech Source — Precision in Every Part